Project Configuration
| Project Description | : | Coal Gasification based Ammonia Urea Complex | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capacity | : | Ammonia | : | 2200 TPD |
| : | Urea | : | 3850 TPD | |
| Project Cost | : | Approximately INR 13,277 crores | ||
The project broadly consists of Coal Gasification Unit, Ammonia Plant with design capacity of 2200 MTD and Urea Plant with design capacity of 3850 MTPD along with associated facilities. The project will have an output of 1.27 MMTPA of ‘Neem’ coated prilled urea using coal as feedstock. The total estimated cost for setting up New Coal based Ammonia-Urea Complex at the existing plant site of FCIL is approx. INR 13,277 cr. which will be financed through equity from shareholders and debt from financial institution in Debt: Equity ratio of 72:28. The unit will utilize about 2.5 MMTPA coal from Talcher Mines. There is also provision of blending up to 25% Pet-coke to handle high ash content in coal. The pet-coke requirement is about 0.33 MMTPA and will be largely made available from Paradip Refinery of Indian Oil Corporation Ltd. (IOCL) for which TFL has already executed a MoU with IOCL.
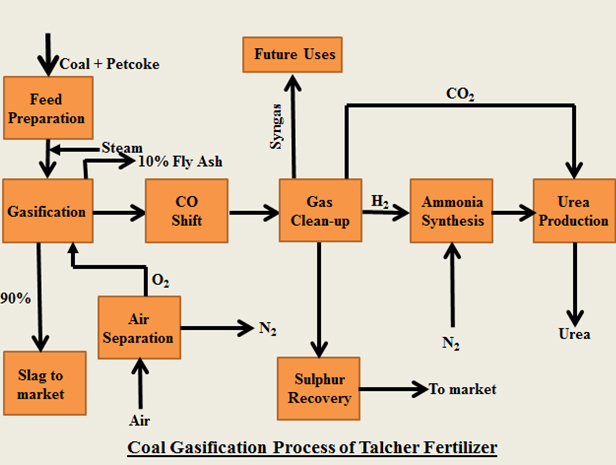
Talcher Fertilizers Ltd. (TFL) is using Coal Gasification for production of Ammonia/Urea. Pollutants like Carbon Dioxide is recycled for production of Urea and other by – products like Sulphur are recovered and are marketed. Further, ash is converted to inert slag which is essentially non – hazardous.
Conversion of Coal to Ammonia/Urea using gasification process involves following Unit Operations:
i. Coal preparation
Coal is milled to fine particles and dried to improve conversion efficiency before being fed into the gasifier.
ii. Air Separation
The air separation unit separates oxygen from air to help facilitate the reaction in the gasifier. The separated nitrogen is used as feed for producing ammonia synthesis gas.
iii. Gasification
Gasification converts coal to raw yngas at a high efficiency by partial oxidation of coal with oxygen to mainly carbon monoxide and hydrogen. The coal ash is melted and recovered as a marketable stable glassy slag.
3C(coal) +O2 + H2O + → H2 + 3CO
iv. CO Shift Concersion
In the water gas shift reaction, carbon monoxide in the syngas reacts with water to form carbon dioxide and hydrogen. High purity hydrogen is required for ammonia synthesis.
CO + H2O → CO2 + H2 (water gas shift reaction)
v. Gas Clean – up (CO2 and Sulphur removal)
The raw syngas contains traces of impurities like trace minerals, particulates and Sulphur as well as carbon dioxide that are removed in the cleanup section. Sulphur can be marketed and Carbon Dioxide is used in Urea production.
vi. Ammonia synthesis
In the ammonia synthesis, hydrogen and nitrogen react in the presence of a catalyst to form ammonia.
vii. Urea production
The ammonia is reacted with the carbon dioxide which was removed from the syngas in the gas cleanup section to produce urea melt. The urea melt is then concentrated, prilled and bagged before dispatch